What Is the Ecliptic?
The ecliptic is the Sun’s path through the starry background of the sky. The Moon and planets follow a similar track.
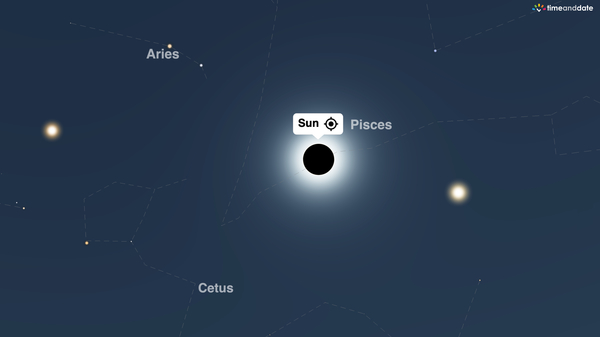
The Sun’s position relative to the stars is revealed during the darkness of a total solar eclipse. In this Night Sky Map view of totality over the US city of Dallas—during the upcoming solar eclipse of April 8, 2024—the Sun is shown to be in front of the constellation Pisces. It forms a nearly straight line with the bright planets Venus (right) and Jupiter (left) in the sky, revealing the path of the ecliptic.
©timeanddate
The ecliptic is the name given to the path the Sun follows through the stars and constellations over the course of a year.
We can’t see the stars behind the Sun because of the bright blue sky. The only exception to this is when the sky turns dark during a total solar eclipse.
The Wandering Sun, Moon, and Planets
The pattern of stars in the sky is fixed: the stars are so far away, they don’t appear to move relative to each other.
Against this fixed starry background, the Sun, the Moon, and the planets do appear to move, because they are much closer to Earth.
How close are the planets compared to the stars?
The nearest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri: it is 4.24 light years away. This means the light from Proxima Centauri takes about 4 years and 3 months to reach us.
By contrast, light reflected from Saturn—the farthest of the planets visible with the naked eye—takes only about 1 hour and 15 minutes to reach us.
The Path of the Sun
Although no stars are visible in the bright daytime sky, the names of the constellations the Sun passes through are well known (except one) as the constellations of the zodiac:
- Pisces
- Aries
- Taurus
- Gemini
- Cancer
- Leo
- Virgo
- Libra
- Scorpius
- Ophiuchus
- Sagittarius
- Capricornus
- Aquarius
The zodiac is the name given to the strip of sky that runs along either side of the ecliptic. The zodiacal constellation that is not so well known is Ophiuchus.
Even though the Sun spends more time in Ophiuchus than it does in Scorpius, Ophiuchus was left out when the zodiac was divided into its 12 traditional ‘signs’ about 2500 years ago.
From Higan to Chuseok: Holidays connected to astronomic events
The Sun Does Not Travel Alone
The solar system is generally flat: the planets, and most of their major moons, orbit in more or less the same plane. (A plane is a flat surface, like a disk.)
This means that to us on Earth, the Moon and planets also tend to follow the Sun’s ecliptic path through the sky.
As a result, whenever we see them in the sky, the Sun, the Moon, and the planets roughly form a straight line. This line is the ecliptic.
How bright is the Sun on other planets?
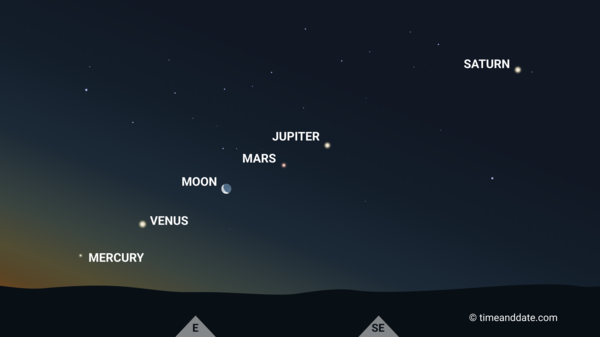
This Night Sky Map view of the Moon and planets over New York in the early morning of June 24, 2022, clearly shows the ecliptic. The roughly straight line formed by the planets continues downward to the Sun, which lies beneath the horizon to the left of Mercury.
©timeanddate.com
The Ecliptic from an Outer-Space Perspective
Astronomers also explain the ecliptic from a different perspective, looking at the solar system from outer space.
The apparent motion of the Sun along the ecliptic is a result of Earth’s movement around the Sun. Another way to think about the ecliptic is, therefore, to say it is Earth’s orbital plane projected onto the celestial sphere.
Earth’s axis is tilted, so the plane of the ecliptic is inclined by about 23.4 degrees to the celestial equator. This angle is called the obliquity of the ecliptic, or axial tilt.
A Multi-Speed Solar System
Different celestial bodies move along the ecliptic at different speeds. The Sun takes one year to complete a full lap through the various constellations, but Saturn takes about 30 years.
The Moon, on the other hand, needs only 27.3 days to complete one full tour of the starry background. This is called a sidereal month.
The hidden patterns of Venus’s movement across the sky
Meetings in the Sky
The Sun, the Moon, and the planets often meet as they travel along the ecliptic. These events are called conjunctions. A famous example is the Great Conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn in December 2020.
A special kind of conjunction happens when the Sun and the Moon meet in the sky—the result is a solar eclipse.
Video: In this video of the 2020 Great Conjunction, as seen from New York during the early evening, Jupiter sweeps by Saturn as the pair travel along the ecliptic. Again, the line of the ecliptic continues downward to the Sun, which lies beneath the horizon to the right.
timeanddate.com
“Ecliptic” Comes from “Eclipse”
Since the Moon passes by the Sun once a month, at New Moon, why don’t solar eclipses happen every month?
It’s because the Moon’s orbit is slightly tilted (by about 5 degrees) to Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
As a result, although the Moon generally follows the Sun’s ecliptic path, it is normally a little above or below it. A solar eclipse can only take place when the New Moon crosses the ecliptic.
In fact, this is the reason why the Sun’s path across the sky is called the ecliptic: it comes from the Greek word ekliptikos, meaning “of an eclipse.”